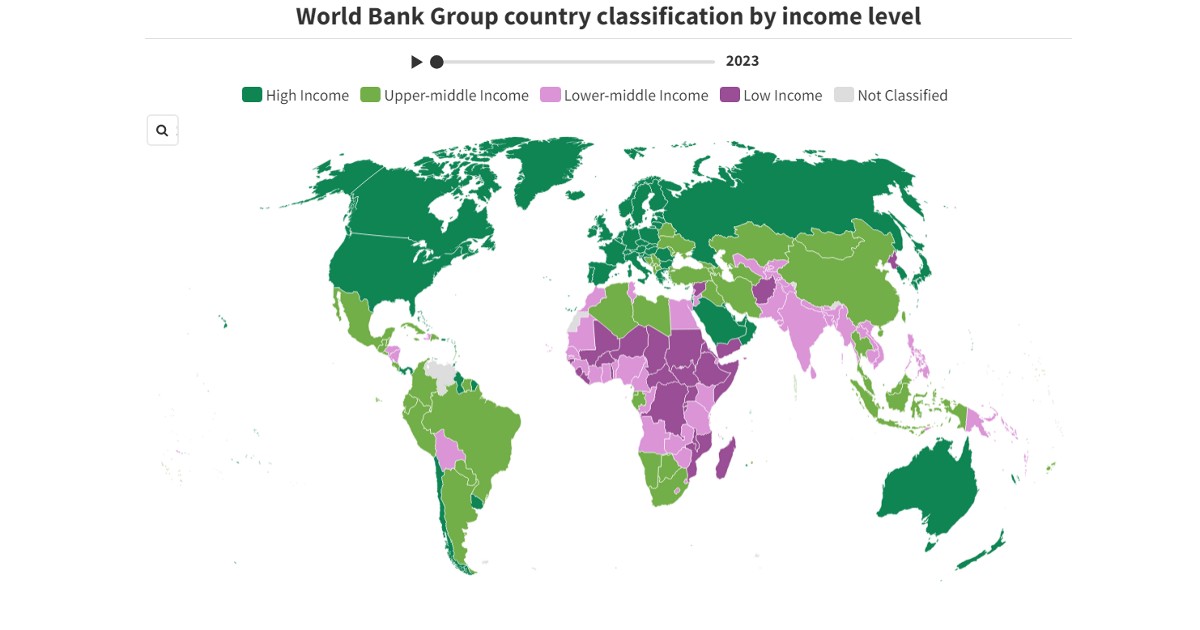
The World Bank Group categorizes the world’s economies into four income groups: low, lower-middle, upper-middle, and high. These classifications are updated annually on July 1st, based on the Gross National Income (GNI) per capita of the previous year. GNI is measured in US dollars using conversion factors based on the Atlas method introduced in 1989. The World Bank’s income classification system aims to provide insight into a country’s level of development by utilizing GNI per capita as an indicator of economic capacity.
Since the late 1980s, the classification of countries into income categories has undergone significant changes. In 1987, 30% of countries were classified as low-income and 25% as high-income. Fast forward to 2023, and the percentages have shifted to 12% in the low-income category and 40% in the high-income category. However, these shifts vary greatly among different regions of the world.
In recent years, there has been a noticeable trend towards fewer low-income countries and more high-income countries. This shift reflects changes in global economic development and growth patterns. As countries strive to improve their economies and living standards, they may move up in income classification over time. By using GNI per capita as a benchmark, the World Bank is able to track and analyze these shifts in income categories among countries worldwide.
Overall, the World Bank’s income classification system provides a useful framework for understanding the economic development of different countries and regions. It highlights the progress that many countries have made in improving their income levels and living standards, while also identifying areas where further development and support may be needed. As the global economy continues to evolve, the World Bank will continue to monitor and update its income classifications to reflect these changes accurately.