- Fri. Apr 26th, 2024
Latest Post
The prevalence of terms like “commendable” and “meticulous” points to the widespread use of ChatGPT in numerous scientific studies
The librarian, Andrew Gray, has discovered a surprising trend in scientific studies published last year. He found that the use of certain words like meticulously, intricate, commendable, and meticulous had…
New Aviators Sports Bar launches in Mandan
Aviators is the newest business in Mandan, located at 202 West Main Street. The sports bar is owned by a group of five individuals, one of whom is Ryan Deichert,…
WellSpan Health Medical Records
Under the Health Insurance Portability and Security Act (HIPAA), you have the right to view your medical record and request changes to it. One way to access your health information…
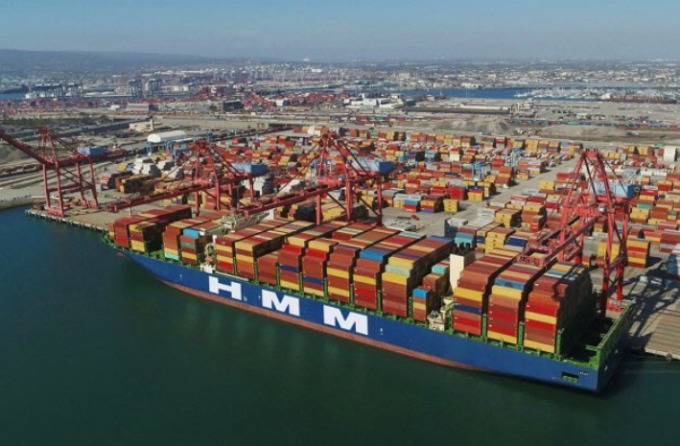
AI technology improves maritime safety using HMM
HMM Co., South Korea’s leading sea carrier, made an announcement on Friday regarding their adoption of an advanced AI image analysis solution called ‘Deep Eyes’. This new technology, developed by…
5-HTP Active Ingredient Can Improve Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
5-HTP, derived from medicinal herbs originating from Africa, has been shown to help improve symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome, also known as spastic colon. The active ingredient, 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), is…
John Constable: The Link Between Art and Technology in the 19th Century
Scientists at the University of Bradford are utilizing groundbreaking new methods to determine if three newly discovered paintings may have been created by John Constable, a renowned 19th-Century artist known…
Kaufmann named finalist for 2024 Presidential Awards for Excellence in Mathematics and Science Teaching | Local News, Sports, and Employment opportunities
Two Iowa educators have been named as 2024 finalists in the Presidential Awards for Excellence in Mathematics and Science Teaching by the Iowa Department of Education. The finalists this year…
Exploring Alaska’s Sports History: Induction into the Alaska Sports Hall of Fame
Eagle River’s multi-sport athlete Bobby Hill will be inducted into the Alaska Sports Hall of Fame on April 30. Harlow Robinson, the executive director of Healthy Futures and the Alaska…
New Exhibit at Functional Fabric Fair Showcases Cutting-Edge NASA Technology in Fabrics
Functional Fabric Fair, powered by PERFORMANCE DAYS, concluded another successful show at the Oregon Convention Center in Portland, Ore from April 17-18. The event attracted 2,100 attendees and featured over…
What is it about broccoli that kids don’t enjoy?
Leo Outamaa, 11, and Broccoli have differing opinions on the vegetable. Even some adults don’t like broccoli, with one former president of the United States, George H.W. Bush, publicly naming…