- Fri. Apr 26th, 2024
Latest Post
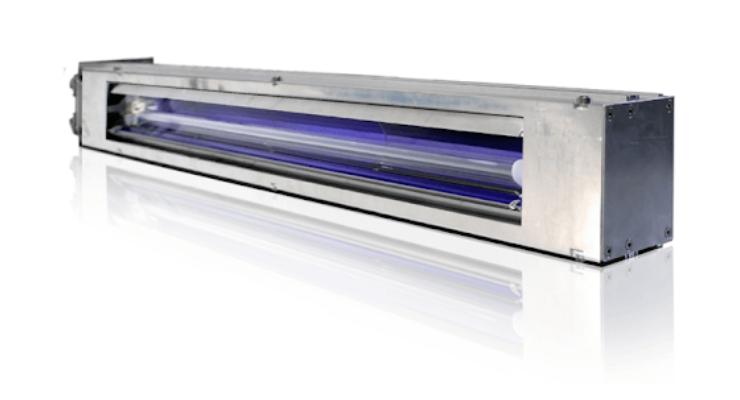
IST America Unveiling Latest Products at RadTech UV&EB Technology & Conference
ISTA, a global supplier of UV and LED light curing technology, will be participating in the upcoming RadTech UV&EB Technology & Conference in Orlando, FL from May 20-22. They will…
Federal Reserve’s Favorite Inflation Gauge Indicates Ongoing Rise in Prices
Today’s report on inflation may suggest that rate cuts by the Federal Reserve are less likely in the near future. The annual inflation rate rose to 2.7% in March, moving…
West Monroe Beautiful provides grants for local businesses to maintain their appearance.
Keep West Monroe Beautiful has introduced the “Next Level Business Grant” program for local businesses in West Monroe, Louisiana. In collaboration with the City of West Monroe and the West…
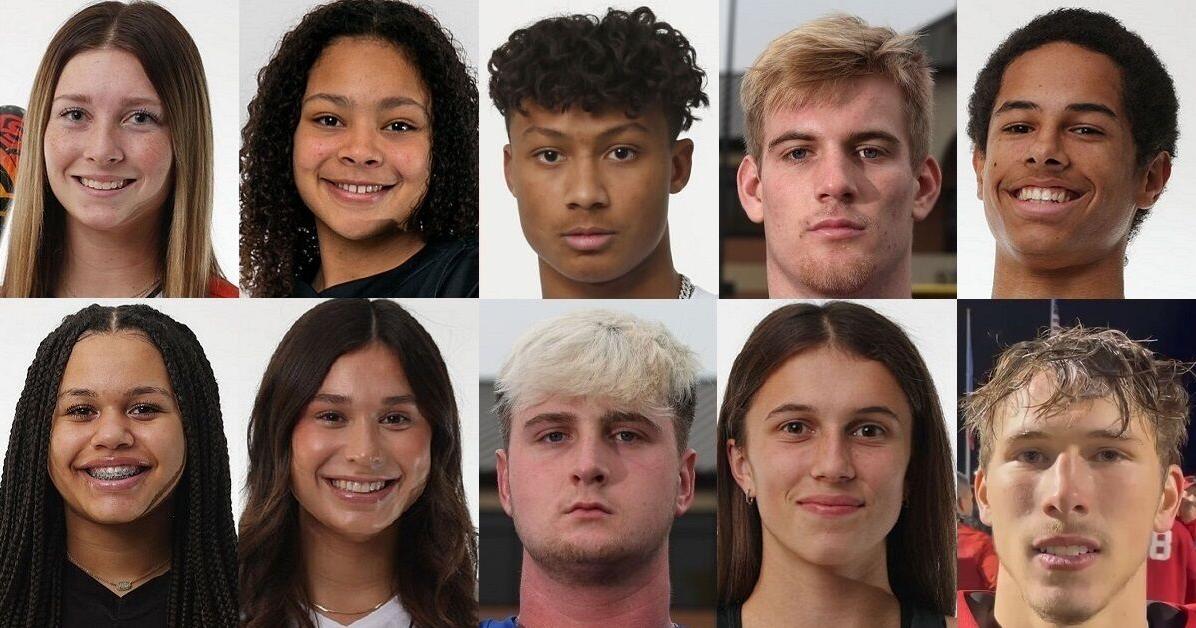
Finalists for the 2023-24 All-World Athlete of the Year Award in Football, Basketball, Wrestling, Swimming, Cross Country, Volleyball, and Softball
The Tulsa World is once again recognizing the top high school athletes in the Tulsa area with the All-World Awards. Finalists for winter sports will be announced this week, including…
CBS Sports and Pluto TV introduce Champions League Soccer FAST Channel
Real Madrid player Jude Bellingham was seen celebrating during the UEFA Champions League quarter-final against Manchester City. The game was intense and full of action, with both teams giving it…
Christian Coleman from the USA Anticipates Usain Bolt’s 100m World Record Being Broken in the Near Future
In August 2009, Bolt set a new record while competing at the World Championships in Berlin. Just a year before that, he had achieved a new world record of 9.69,…
Health and Fitness Expo to Open Before Memorial Marathon Weekend
Before the start of the Oklahoma City Memorial Marathon races, participants and guests have the opportunity to attend the Health and Fitness Expo at the Oklahoma City Convention Center. The…
Players in the NFL now have the choice to wear Guardian Caps during games
The NFL has now allowed players to wear Guardian Caps during practice sessions, a change from their previous stance of prohibiting them during games. The decision was made in an…
TikTok suspends its paid video-watching app Lite
TikTok has decided to suspend its Lite app, which allowed users to earn money by watching videos or recommending other users. The European Commission threatened to block the app due…
Official launch of the Xiaomi 14 Ultra in Peru: Discover the features and price of the Leica camera smartphone
Xiaomi recently launched its highly anticipated Xiaomi 14 series during an event in Santiago de Chile, where the new smartphones were introduced and made available in the country. Along with…
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-12466528093-bb52afb615994ff8983eb8cf1482a15c.jpg)


